Public Works & Infrastructure
Public Works & infrastructure are essential components of local and state government responsibilities. They involve the construction, maintenance, and management of vital public facilities and services such as roads, bridges, water supply, and waste management. Effective infrastructure planning ensures communities have the necessary resources for economic growth and quality of life. This directory provides articles on public works and infrastructure and related topics like Transportation, which explores the development of efficient systems for moving people and goods.
Turn federal changes into opportunities for your community
The Enhancing First Response Act would recognize dispatchers’ lifesaving role and improve emergency communications infrastructure
The annual grant program awards $20 million across more than 600 public libraries in Illinois
It’s unclear what the consequences of the city-parish’s violations will be, or the feasible fixes
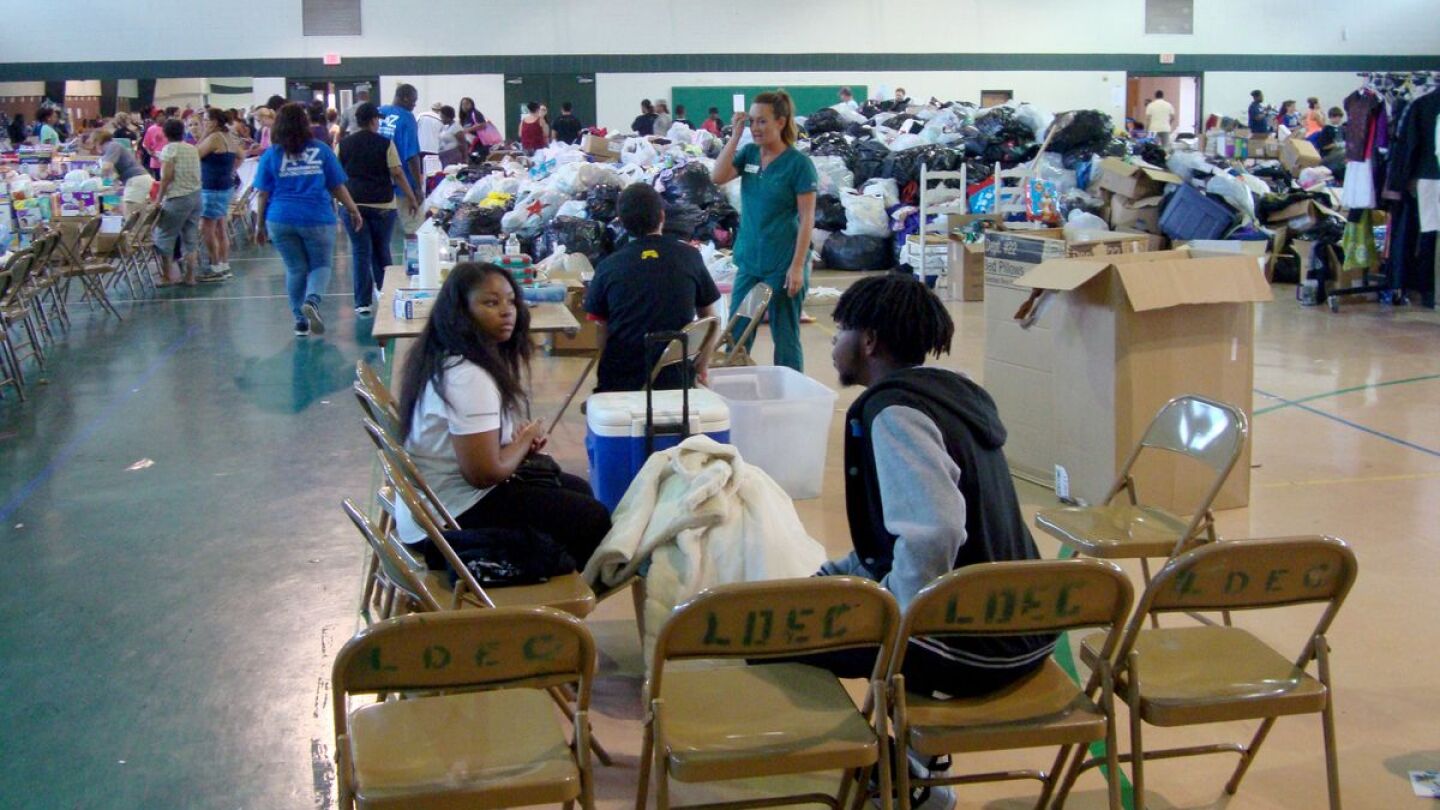
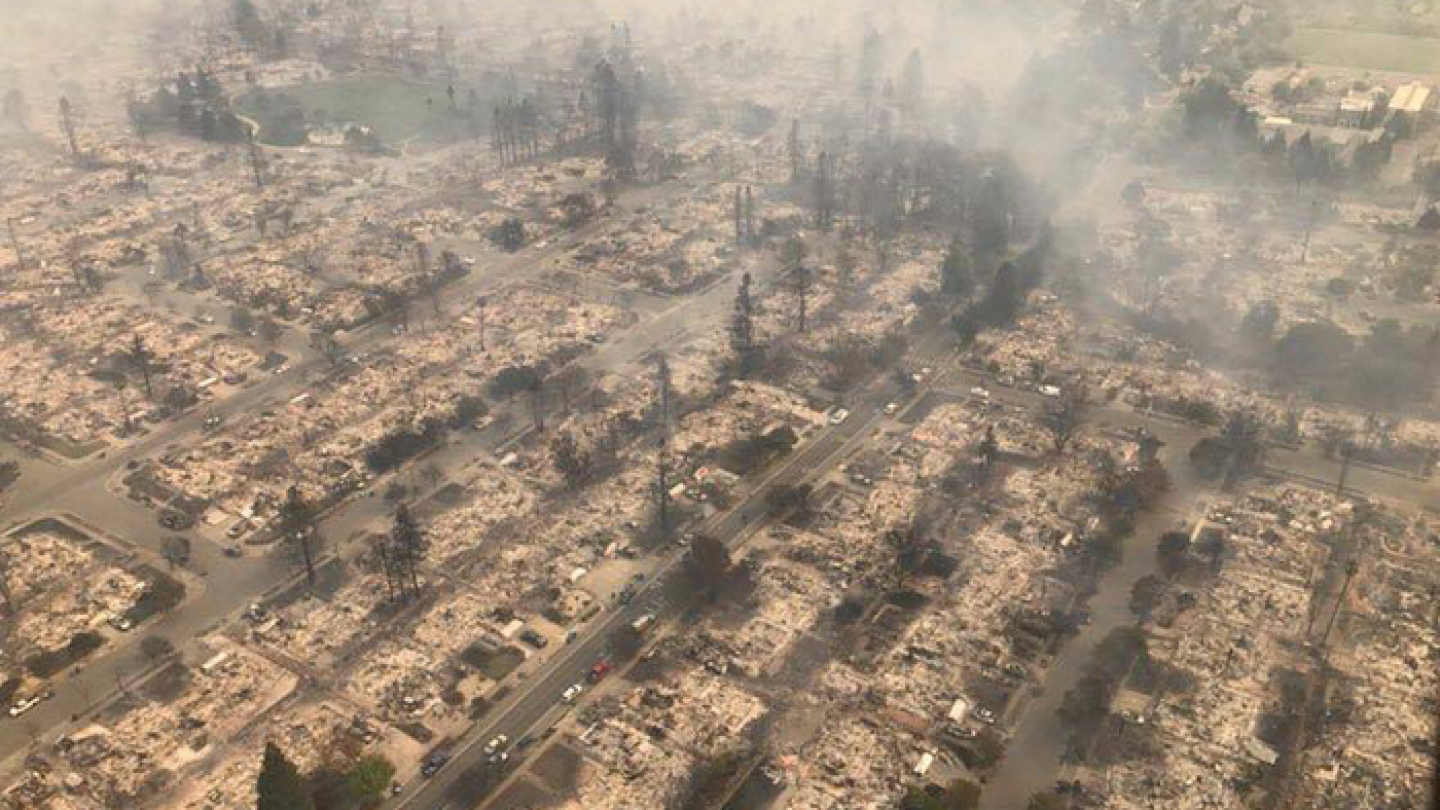
A new study identifies critical issues that communities should consider after a wildfire
An in-depth study on e-scooter traffic safety reveals where and why most collisions occur
Nearly a year ago, a consultant hired by the city recommended the structure be closed immediately due to a “magnitude of code violations”
While there has only been one officially recorded case of the UK variant in Missouri, wastewater samples tell a different story
Someone briefly increased the amount of sodium hydroxide, also known as lye, by remotely accessing a city computer
The cost includes damage to garbage trucks, street lights and traffic signals
Maryland State Police confirmed they caused much of the damage during a 40-hour standoff with an armed suspect
The crowd threw bottles at cops and put metal bars in the street to try to damage police vehicles, officials said
From mitigating contagions to combating the opioid crisis, surveilling wastewater should be part of every city’s public health toolbox
First responders said they have had to slowly navigate large apparatus around the potholes to respond to many emergencies at the park’s pond and cliff-hiking area
Gov. Jim Justice initially allocated $100 million to maintenance of 95 roadways he calls “COVID-19 highways”
The first responders on bicycles will be able to respond to medical emergencies more quickly than on larger apparatus
The water regulation changes, finalized last week, will limit states’ reviews of natural gas and oil pipelines and other projects impacting waterways
Rep. Peter DeFazio called the Moving Forward Act a “transformational investment in American infrastructure that will create millions of jobs”
New survey data from over 1,100 municipalities shows that the national economic recovery is at even greater risk than previously thought
MOST POPULAR
- Mass. public health officials hesitate to endorse nalmefene
- How Witch City teaches its dark history at Halloween
- Worried that remote access can lead to increased cybersecurity vulnerabilities?
- The big picture: FEMA, DOGE and your local fire department
- Conn. governor signs law creating fund to aid families of fallen officers